What Is A Hillshade Map? A Comprehensive Guide
Hillshade maps, also known as terrain maps, represent a fascinating intersection of art and science in cartography, offering a three-dimensional portrayal of landscapes on a two-dimensional surface.
These maps use shading techniques to visualize terrain, highlighting elevation changes and providing a realistic representation of the Earth's surface.
In simpler terms, terrain map prints portray changes in elevation, such as those in mountainous terrains or valleys, using shadows, appearing 3D even on plain paper.

The History of Terrain Maps
The history of terrain maps dates back thousands of years, with early civilizations developing rudimentary forms of topographic representation to navigate landscapes and plan settlements.
Some of the earliest known examples come from ancient Mesopotamia, where clay tablets dating back to around 2300 BCE depicted land divisions and elevation changes using simple markings.
Early Advances
The Greeks and Romans later advanced mapping techniques, incorporating relief shading and contour-like methods to illustrate mountainous regions in military and administrative cartography.
The ancient Chinese also created sophisticated maps that included elements of topography, using brushwork and text annotations to depict mountains and rivers as early as the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE).
The Renaissance & Beyond
During the Renaissance, terrain mapping saw significant advancements with the emergence of perspective and mathematical approaches to cartography.
Leonardo da Vinci was among the first to use hachure marks—short parallel lines indicating slope direction and steepness—while European surveyors developed triangulation methods to measure and represent elevation more accurately.
By the 18th and 19th centuries, the development of contour lines, attributed to figures like Charles Hutton and J.L. Dupain-Triel, revolutionized terrain representation by providing a standardized way to show elevation on flat maps.
This innovation was particularly crucial for military strategy, engineering projects, and land management, as accurate topographic details allowed for better planning of roads, railways, and fortifications.
The 20th century ushered in further improvements with aerial photography and satellite technology, enabling cartographers to produce highly detailed topographic maps at unprecedented scales.
Governments and scientific organizations, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS), began systematically mapping terrain to support geological studies, infrastructure development, and environmental conservation.
The advent of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the latter half of the century transformed terrain mapping into a digital, data-driven field, allowing for real-time analysis and dynamic 3D visualizations.
The Terrain Maps of Today
Today, terrain maps are integral to countless applications, from navigation and urban planning to environmental monitoring and disaster response.
With continuous advancements in artificial intelligence and remote sensing, the future of terrain mapping promises even greater accuracy and usability across a wide range of disciplines.

Understanding Hillshade Maps
Hillshade maps are a powerful tool in topographic visualization, providing a three-dimensional appearance to flat maps by simulating the way light interacts with terrain.
By using variations in shading, these maps enhance the perception of elevation changes, helping geographers, cartographers, and planners analyze landscapes more effectively.
They are widely used in applications such as GIS, environmental studies, and land-use planning, offering a clear and intuitive way to interpret complex topographic features.
How Hillshade Maps Are Created
Hillshade maps are generated by applying a mathematical model that simulates the angle and intensity of sunlight over a digital elevation model (DEM).
The process involves assigning light and shadow to terrain features based on a defined light source, typically set at an azimuth of 315° (northwest) and an altitude of around 45°.
Pixels in the map receive varying degrees of shading depending on the slope and orientation of the terrain relative to the light source.
Steep, north-facing slopes appear darker, while south-facing slopes are brighter, creating a realistic representation of hills, valleys, and ridges.
Advanced GIS software automates this process, allowing users to adjust parameters such as sun angle, altitude, and vertical exaggeration for customized visualizations.
The Science Behind the Visualization Technique
The effectiveness of hillshade maps lies in the way human vision interprets light and shadow to perceive depth.
Our brains naturally associate brighter areas with surfaces facing a light source and darker areas with those in shadow, a principle rooted in photorealistic shading techniques.
This method, known as shaded relief or hill-shading, enhances depth perception, making it easier to recognize landforms even without contour lines.
The technique also relies on altitude scaling to exaggerate subtle variations in elevation, ensuring that terrain features remain visible even in relatively flat regions.
Combined with other layers, such as contour lines or land cover data, hillshade maps provide a comprehensive view of the landscape for a wide range of analytical purposes.
Different Types of Hillshade Maps
Hillshade maps can be categorized based on the method of shading and the number of light sources used.
Single-direction hillshade maps utilize one primary light source, typically positioned in the northwest, to cast shadows in a uniform direction. This method provides a clear and easy-to-read visualization but can sometimes obscure terrain details if the light source aligns with slope orientations.
Multi-directional hillshade maps, on the other hand, combine shading from multiple light angles, reducing harsh contrasts and enhancing detail visibility across various terrains.
Some hillshade maps also incorporate colorized elevation shading, where colors represent different elevations, further improving the interpretability of the terrain.
Recent advancements in GIS technology have introduced dynamic hillshade maps, which allow users to interactively adjust lighting conditions to explore terrain from different perspectives.
Hillshade mapping continues to evolve with improvements in remote sensing and 3D modeling, making it an indispensable tool for modern cartography, environmental analysis, and spatial planning.
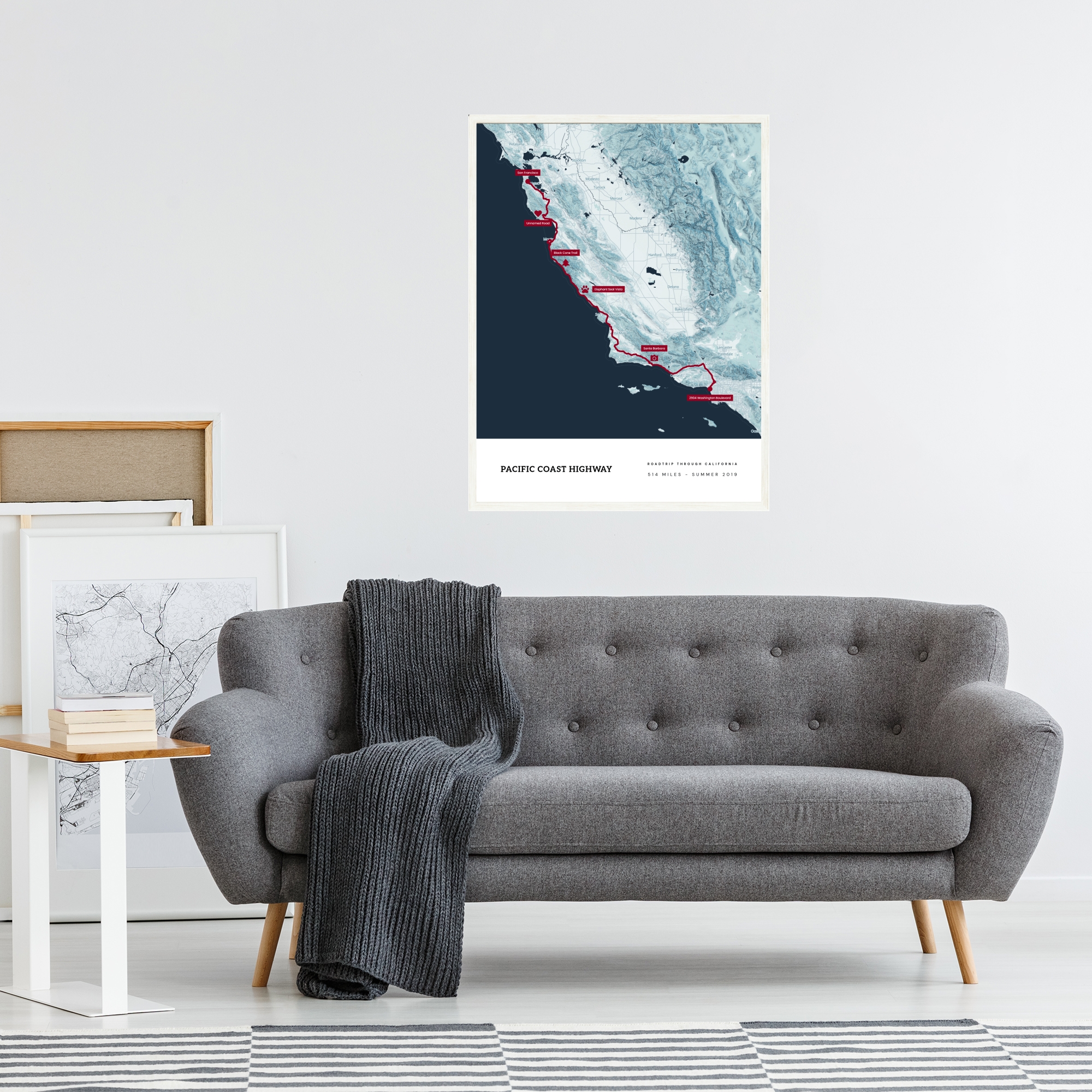

Components of a Hillshade Map
Elevation data forms the core foundation of hillshade maps. It represents the vertical distance between a specific point on the Earth's surface and a reference datum, often sea level.
This data is gathered using various methods, including aerial surveys, satellite imaging, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and radar technologies.
The elevation information collected is instrumental in rendering a visual depiction of the landscape's undulations and contours, contributing to the creation of accurate hillshade maps.
A crucial aspect of hillshade mapping involves defining the light source direction. Simulating natural lighting conditions, the angle and orientation of the sun in relation to the landscape are determined.
Shadows are cast by elevated features such as hills, mountains, and ridges, depending on the angle of incidence of the light source.
These shadows, combined with the light hitting slopes facing the light source, yield a realistic depiction of the terrain's three-dimensional features.
Color gradients and texture are fundamental in conveying elevation changes on hillshade maps.
Typically, these maps use monochromatic shading or color schemes to represent different elevations. Darker shades or colors denote lower elevations, while lighter tones signify higher elevations.
This differentiation through color gradation helps to visualize changes in terrain height. Texture is employed to portray surface roughness or smoothness, enhancing the map's visual appeal and aiding in the interpretation of terrain features.
Integrating color gradients and texture facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape's topography on the map.
Uses and Applications
Hillshade maps are integral components within Geographic Information Systems (GIS), facilitating the overlaying of diverse geographic data layers.
This integration empowers professionals in various fields, including urban planning, resource management, and infrastructure development, by enhancing spatial analysis and decision-making processes.
Environmental Studies and Conservation Efforts
Within environmental studies, hillshade maps play a pivotal role in assessing terrains for land use, identifying erosion-prone areas, and strategizing conservation efforts.
These maps aid scientists and land managers in making informed decisions aimed at preserving natural habitats and ecosystems.
Outdoor Recreation and Urban Planning
For outdoor enthusiasts, hillshade maps are invaluable in route planning, particularly for hiking and various outdoor activities.
Moreover, in urban planning contexts, these maps provide a comprehensive understanding of topography, aiding in infrastructure development and the creation of recreational spaces.
Modern Memory Keeping
While hillshade, or terrain maps, have many practical uses, their newest application stems from the art of memory keeping. These maps can be used to create custom artwork inspired by adventures, experiences, and other personal stories.
Here at MixPlaces, we specialize in incorporating these mapping tools to give you a one-of-a-kind, fully personalizable piece that tells stories near and dear to your heart.
From travel posters to hiking posters and even national parks posters, you can create your own map of the exact location you wish, adding your own text, colors, and other elements to make it your own.

The Future of Hillshade Mapping
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping the future of hillshade mapping.
Ongoing advancements in remote sensing technologies and high-resolution elevation data collection methods contribute to generating more accurate and detailed hillshade maps.
LiDAR technology, for instance, offers precise elevation data, enhancing the quality and accuracy of hillshade representations.
Some future trends and advancements in Hillshade Mapping:
-
Advancements in Remote Sensing Technologies: Continuous progress in remote sensing and elevation data collection methods, particularly LiDAR technology, enhances the accuracy and detail of hillshade maps by providing high-resolution elevation data.
-
Integration with Diverse Mapping Techniques: Hillshade mapping's potential is maximized through integration with other datasets like satellite imagery and multi-layered GIS data. This integration enables comprehensive visualizations, offering a more holistic perspective of landscapes.
-
Evolution of Digital Cartography: Emerging trends in digital cartography, including innovative data visualization methods, augmented reality, and 3D cartography, are set to transform hillshade maps. These innovations promise more interactive and immersive experiences for users, enabling deeper exploration of terrains and landscapes.
Emerging trends in digital cartography signal an exciting future for hillshade mapping.
Innovations in data visualization, augmented reality, and 3D cartography promise to revolutionize the way hillshade maps are perceived and utilized.
The use of immersive technologies and interactive platforms will offer users a more engaging and dynamic experience, allowing for deeper exploration of terrains and landscapes.
Charting Tomorrow: The Evolutionary Horizon of Hillshade Mapping
Hillshade mapping stands as a vital technique in cartography, offering insightful visual representations of terrains and landscapes. Its importance in providing context and depth to geographic information remains indisputable.
Understanding its creation, applications, and limitations illuminates its significance in various fields and its potential for future advancements.
Looking ahead, the future of hillshade mapping is intertwined with technological progress.
Advancements in data collection methods, integration with other mapping techniques, and emerging trends in digital cartography promise to redefine how we visualize and utilize hillshade maps.
This evolution offers exciting possibilities for enhanced accuracy, interactivity, and a deeper understanding of landscapes.
As technology continues to propel cartography into new realms, the use of hillshade maps will likely witness transformative changes.
The fusion of innovative technologies and the continued refinement of hillshade mapping techniques will not only address current limitations but also expand its applications, ensuring its relevance and usefulness in the ever-evolving field of cartography.
This marks the evolution of hillshade mapping, from its historical origins to its present applications and future prospects, cementing its status as a valuable tool in geographic visualization and analysis.
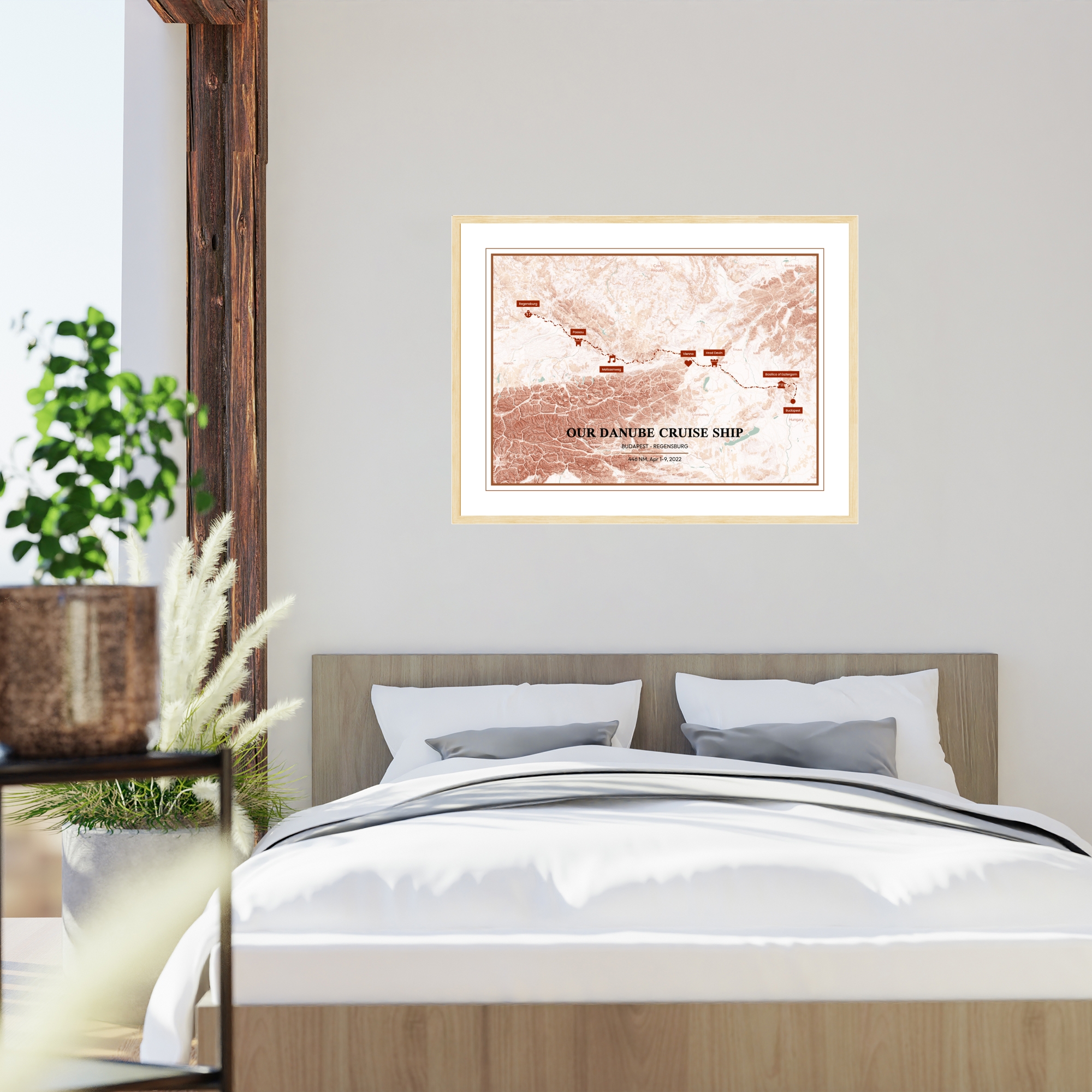

Making Your Own Hillshade Map
Despite all the big, fancy words associated with terrain maps, they’re as easy to make as possible. Especially here at MixPlaces!
To make your own hillshade map, complete with personalizable colors, text, layouts, and more, simply create your own custom map poster with us. Select the “Terrain Map” map type, type in your location, and get customizing!
You can use these maps to commemorate anything, including road trips, hikes, your favorite places, and more, and add markers and routes to make them even more special.
At MixPlaces, we aim to be the best in the mapmaking game, and with super accurate GPS mapping, you can select any region you want, from entire countries or even continents to specific addresses.
Plus, our maps are printed with fade-resistant ink on museum-grade archival paper, so once you create your own terrain map, it’s not going anywhere! It’ll last decades even if displayed under direct sunlight.
What are you waiting for? Create your own terrain map today!