Types of Coordinate Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
In our quest to navigate and map the Earth, coordinate systems serve as the foundation for positioning anything and everything around us.
These systems are not just tools for geographers and sailors; they have permeated our everyday lives through technologies like GPS on smartphones, location tracking for delivery services, personalized coordinates posters, and even the tagging of photos on social media.
Understanding the various types of coordinate systems and their applications is essential in a world that is increasingly location-aware.
A coordinate system is a mathematical framework used to precisely determine and represent positions of points in a space, enabling accurate localization and measurement. It employs a set of numbers or coordinates to specify the location of a point relative to a reference frame or origin.
In navigation, coordinate systems offer a means to accurately pinpoint locations on Earth's surface or in celestial spaces, vital for travel, exploration, and understanding spatial relationships between objects.
What Are Coordinate Systems?
At its core, a coordinate system is a method to identify, express, and map positions of points within a space, which can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D).
The concept underpins various fields, including geography, astronomy, physics, and engineering, allowing for the precise and consistent specification of locations.
Coordinate systems can be broadly classified into two categories: geographic coordinate systems and projected coordinate systems.
Geographic coordinate systems use a three-dimensional surface to define locations on Earth, using latitude and longitude.
Projected coordinate systems, on the other hand, project or convert the Earth's spherical surface onto a flat surface, using a variety of methods to minimize distortion, such as the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Mercator projection.

How We Got Here: The History of Coordinate Systems
The concept of coordinate systems dates back thousands of years, evolving through the ages as civilizations sought better ways to navigate their world and understand the heavens.
The journey from rudimentary methods of marking geographic space to the precise systems we use today is a fascinating tale of scientific progress and innovation.
Ancient Beginnings
The earliest forms of coordinate systems can be traced back to ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians, Greeks, and Egyptians, who developed early methods for mapping the stars and delineating land for agricultural and construction purposes.
However, these were not coordinate systems in the modern sense but rather the precursors to the sophisticated methods we would see later.
The Greek Influence
The concept of using a grid to map the Earth was significantly advanced by the Greeks. Eratosthenes (276-194 BCE), a Greek mathematician, is credited with one of the earliest uses of geographic grids.
He famously calculated the Earth's circumference with remarkable accuracy using simple geometric principles and observations of the sun. However, it was Claudius Ptolemy (100-170 CE), another Greek scholar, who laid the groundwork for the modern coordinate system.
In his seminal work, the Geographia, Ptolemy introduced the concept of using a grid of latitude and longitude to map the known world, dividing the Earth into a system of lines to help describe locations.
Although his maps were not entirely accurate by today’s standards, Ptolemy's method of using mathematical principles to describe geographic space was revolutionary.
The Age of Exploration
The Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries spurred further developments in coordinate systems as European explorers traversed the globe. The need for accurate navigation and mapping of new lands made the concepts of latitude and longitude essential.
Innovations in navigation technology, such as the astrolabe and later the sextant, allowed sailors to determine their latitude by measuring the angle of the sun or stars above the horizon.
The Prime Meridian and Standardization
The establishment of the Prime Meridian was a critical step in the standardization of global coordinate systems. Prior to the late 19th century, different countries used different meridians for navigation and mapping, leading to confusion and inconsistency.
In 1884, the International Meridian Conference held in Washington, D.C., designated the meridian passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, as the Prime Meridian, setting the standard for global navigation.
Modern Advances
The 20th and 21st centuries have seen remarkable advances in the accuracy and application of coordinate systems. The invention of the Global Positioning System (GPS) in the late 20th century revolutionized navigation and mapping.
GPS relies on a network of satellites to provide precise location data anywhere on Earth, using a form of coordinate system that includes not only latitude and longitude but also altitude.
Furthermore, the advent of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has transformed how we visualize and analyze geographic data. GIS combines spatial data with various types of information, allowing for complex analyses of environmental, social, and urban planning issues.

What is Latitude and Longitude?
The most fundamental geographic coordinate system is defined by latitude and longitude.
This system divides the Earth into a grid, where latitude measures how far north or south a point is from the Equator and is represented as lines running parallel to the Equator.
Longitude, on the other hand, measures how far east or west a point is from the Prime Meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England, and is represented as lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole.
When it comes to coordinates, the Earth is divided into 360 degrees of longitude and 180 degrees of latitude (90 degrees both north and south of the equator). Latitude and longitude are traditionally expressed in degrees (°), minutes ('), and seconds (“).
Degrees, Minutes, & Seconds - The DMS System
One way to write spherical coordinates using latitude and longitude is by using the degrees-minutes-seconds (DMS) system.
The Degrees/Minutes/Seconds (DMS) format is an older form of geographical coordinate that splits each degree of latitude and longitude into 60 minutes and each minute into 60 seconds.
This format is especially useful for precision, as it allows for the designation of a location with a high degree of accuracy.
For example, the geographic coordinates for New York City might be expressed as 40° 42’ 51” N for latitude and 74° 0’ 21” W for longitude.
You can look at the DMS format as plotting points on a graph, where your latitude lines run east to west (left to right) and longitude lines run north to south (up and down). When combined, latitude and longitude lines reveal a specific point on the planet’s surface, allowing us to find directions to and from anywhere in the world.
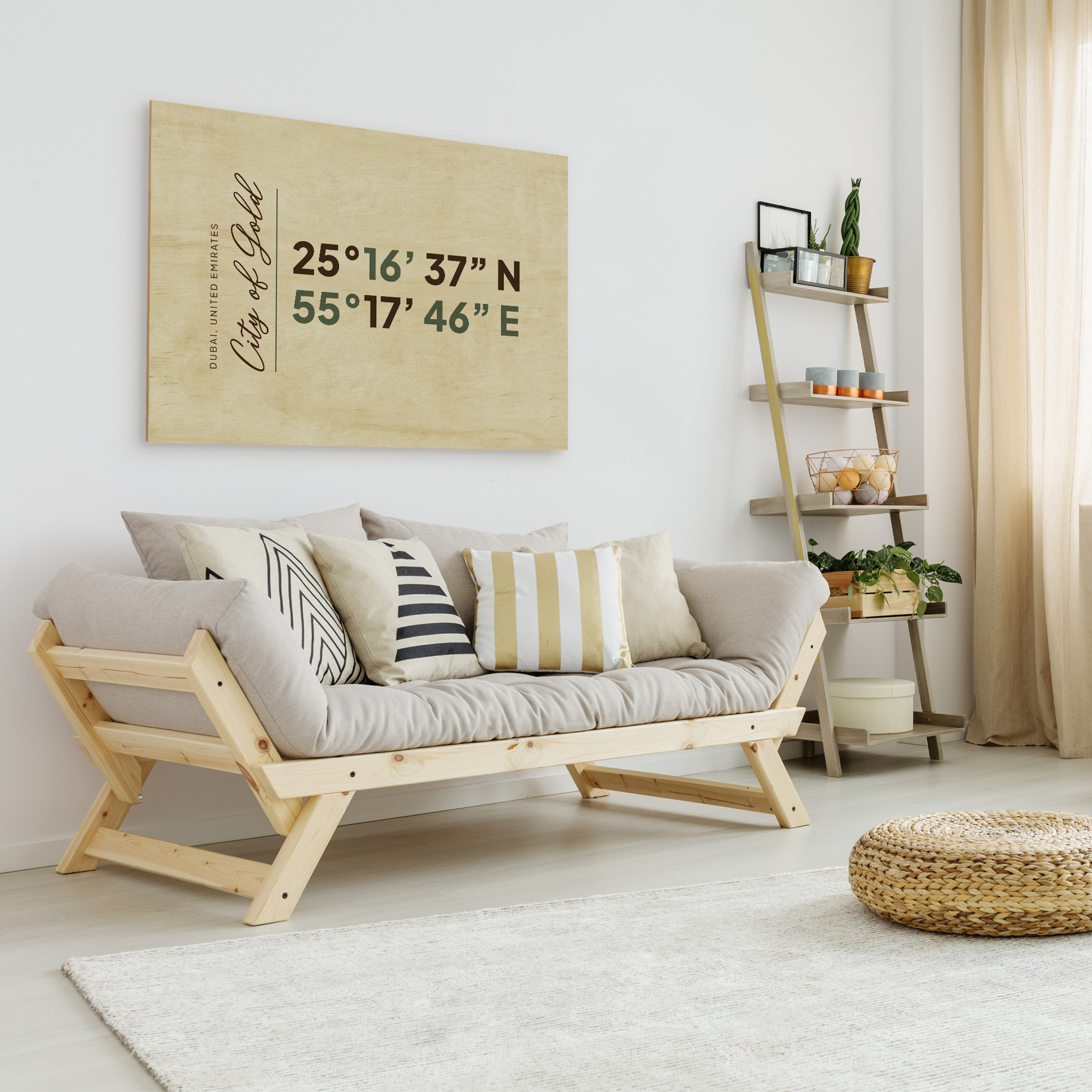

Decimal Degrees - The DD System
Decimal degrees (DD) is a more modern format that expresses latitude and longitude as decimal fractions of a degree.
This format simplifies calculations and is more compatible with digital systems and GPS technology.
For instance, the DMS coordinates mentioned above for New York City might be converted into decimal degrees as 40.714 for latitude and -74.006 for longitude.
This format is not only easier to read but also facilitates more straightforward computations in programming and data analysis.
You can convert DMS to DD and vice versa easily by hand by using the following conversion formula, but it’s even easier to use the FCC’s DMS-Decimal converter tool:
- decimal degrees = degrees + (minutes / 60) + (seconds/3600)
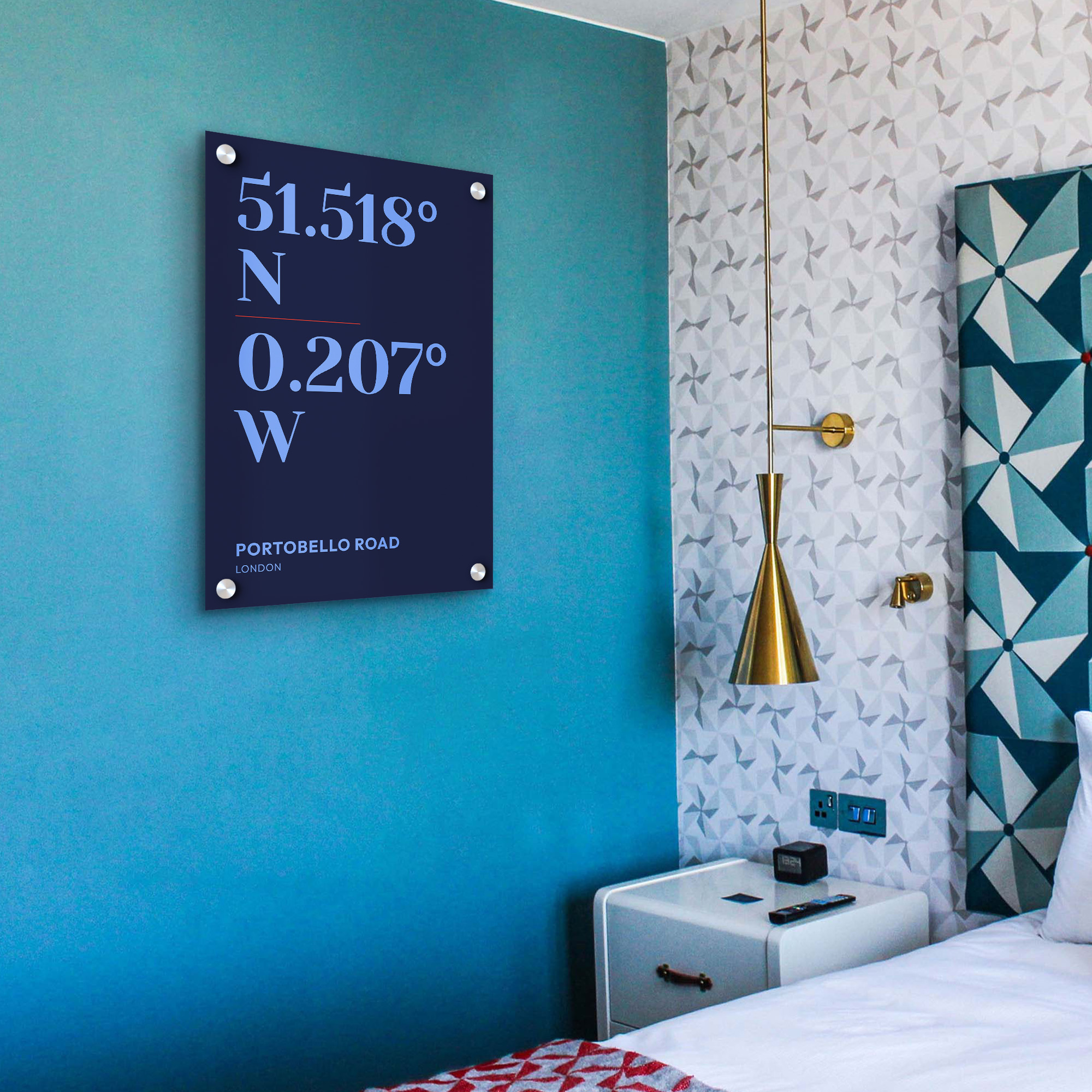

DMS vs. DD: Which is Best?
Choosing between DMS and DD often depends on the application and the audience.
For everyday use, especially in digital and technological applications, DD is preferred for its simplicity and ease of use. However, for specific fields like surveying, navigation, and historical studies, DMS may still be used due to its precision and tradition.
The choice also reflects a trade-off between accuracy and convenience.
While DMS offers a more detailed representation, it can be cumbersome to work with, especially without the aid of specialized tools. DD, conversely, is much more user-friendly and is supported by most modern GPS and mapping software.
Aesthetics-wise, you can use either type of coordinate system to display a specific location with emotional significance to you. The truth is, if you’re using coordinates for home decor, as a gift, or any other reasons that aren't for real-time navigation, both DMS and DD work. All you need to do is pick which one looks best to you!
MixPlaces Coordinates Posters
While coordinate systems may be a lot of math, and not seem that fun unless you’re going on a GPS-less adventure, they’re not just about latitudes and longitudes. In fact, coordinates can become priceless mementos if utilized right.
At MixPlaces, we take pride in helping you create unique, one-of-a-kind keepsakes that reflect your greatest memories, be it the birth of your child, the location of your wedding, your favorite trips, and more.
With MixPlaces coordinates art, you’ll find a unique way to immortalize your cherished locations as personalized wall art. You can transform your special memories into stunning visual representations using latitude and longitude to mark your favorite places in the world.
Capture the sentiment of where significant life moments occurred – from where you met, got engaged, or tied the knot, to where your most cherished memories were made. Our posters elegantly display the geographic coordinates of these pivotal places, beautifully designed and tailored to your preferences.
Each poster is meticulously crafted to reflect the sentimentality of your chosen location, allowing you to reminisce about the precious moments that hold a special place in your heart.
Coordinates Posters Ideas
From travel posters to gifts for newlyweds, a coordinates poster from MixPlaces can do it all. Elevate your home or office space, make a splash at the gift table, or give your loved ones a unique, creative memento of your special time together.
If you’re in search of some ideas to spice up your— or your loved ones’— walls, here’s some inspiration to get you started!
- The coordinates of your childhood home, hanging wherever you live now, to represent your roots and familial connections.
- The exact spot you met, went on a first date, got engaged, or tied the knot, to represent the place that means so much to your love story.
- The coordinates of your favorite city in the world, from a trip that changed your life.
What are you waiting for? Make your own coordinates poster today!

The Coordinates to Their Heart
Understanding the types of coordinate systems, particularly latitude and longitude, and the formats used to express them, is crucial in a wide range of fields and applications.
Whether for scientific research, navigation, or simply tagging a location on social media, knowing how to read and interpret these coordinates connects us more deeply to the world we inhabit.
Although reading and understanding coordinates has become less essential with the rise of GPS and GIS technologies, coordinate systems can still be helpful in creating beautiful and unique art inspired by life’s most memorable moments.
With our coordinates posters, you can bring your greatest memories to life and adorn your space with the moments that make you who you are.